Scroll Down
About us

When the air we breathe turns into a serious risk
The global risk of virus and bacteria spreading through the air is rising - not only during a pandemic virus outbreak SARS-CoV-2 in 2020. Clean air becomes more and more important as polluted air displays a true health risk for everybody. Since we spend about 90% our time in closed rooms and buildings, being constantly exposed to polluted indoor air can turn into serious lung diseases or even cancer.

Air Quality Solutions
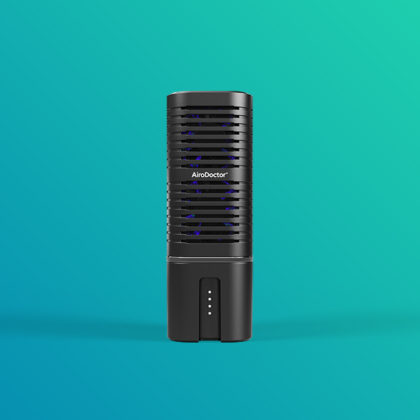
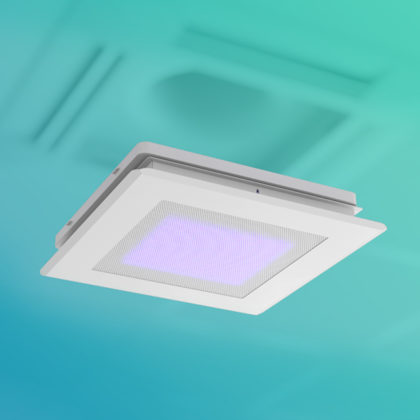
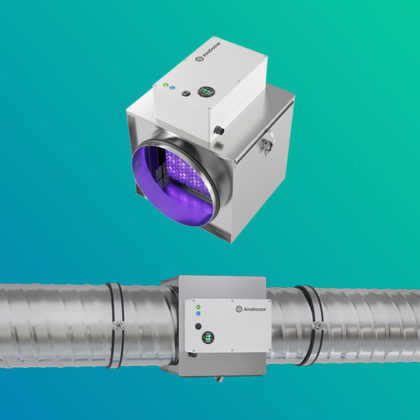
The UV LED air purifier is equipped with a photocatalytic titanium pro filter, which provides clean air that is harmless to the human body by decomposing and removing 99.9% of harmful substances, odor, various pathogenic bacteria and viruses in the air.
- ✔ Eco-friendly UV LED photocatalyst technology
- ✔ No secondary products & no ozone
- ✔ 99.9% decomposition of harmful substances
- ✔ Cost-effective / Low energy consumption

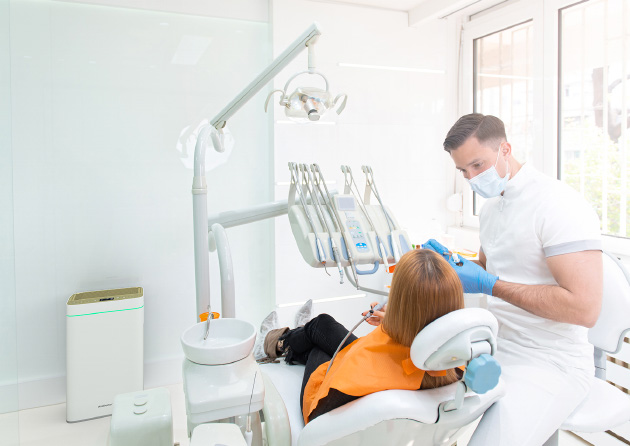
HOSPITAL / CLINIC
- Reduction of the spread of MRSA among visitors and patients & reduction of odor pollution.
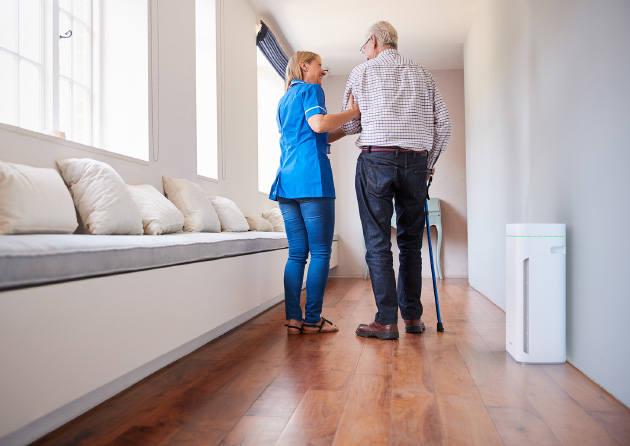

NURSING HOME
- Control of MRSA infections via the respiratory tract & neutralization of odor pollution caused by incontinence patients.
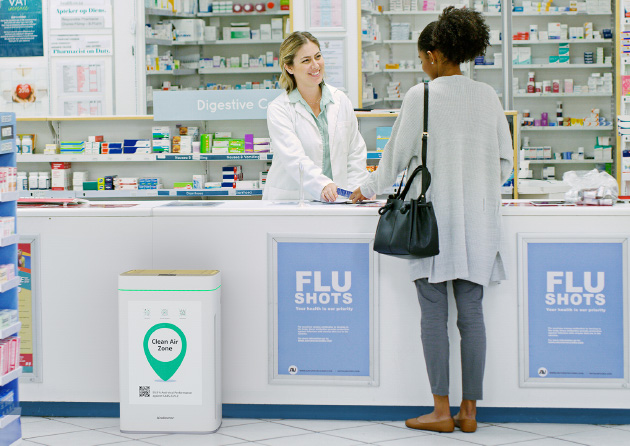

PHARMACY
- Reduction of the risk of infection for visitors and containment of fine dust pollution in public spaces.
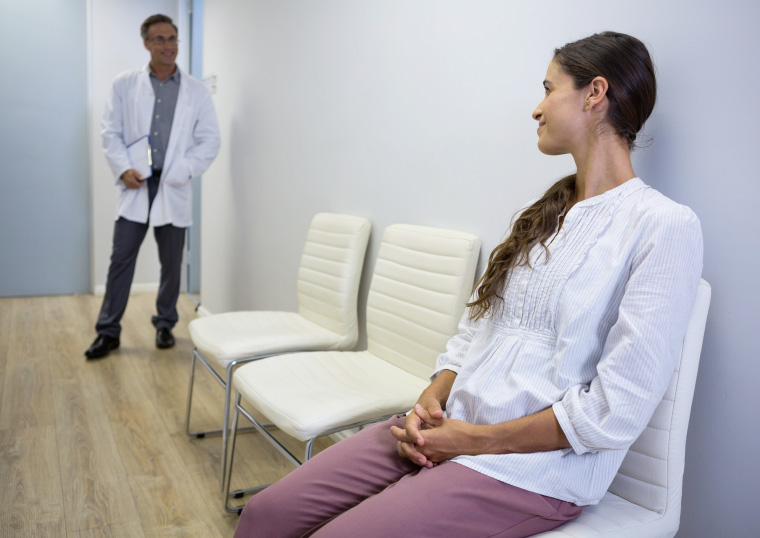

WAITING ROOM
- Reduction of the mutual risk of infection from the air in the waiting room.
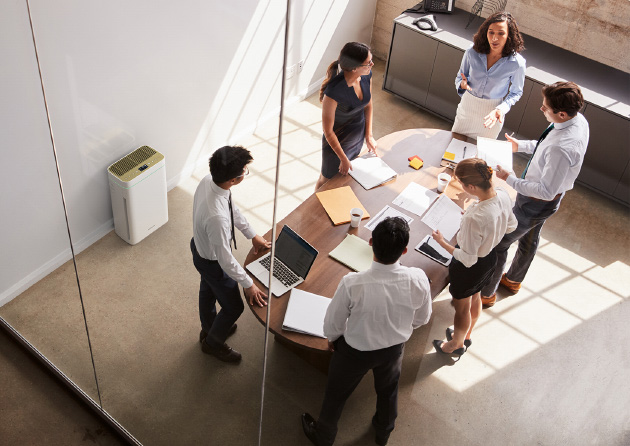

CORPORATE OFFICE
- Improved concentration and healthier indoor air through the filtering of fine dust and gases in the air & reduction of sick leave due to a lower risk of infection among themselves.
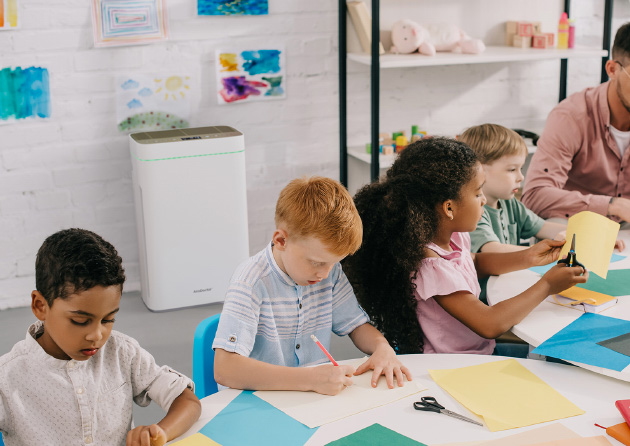

SCHOOL
- Reduced risk of infection among children as well as improved concentration, performance and fewer sick days thanks to healthier air.
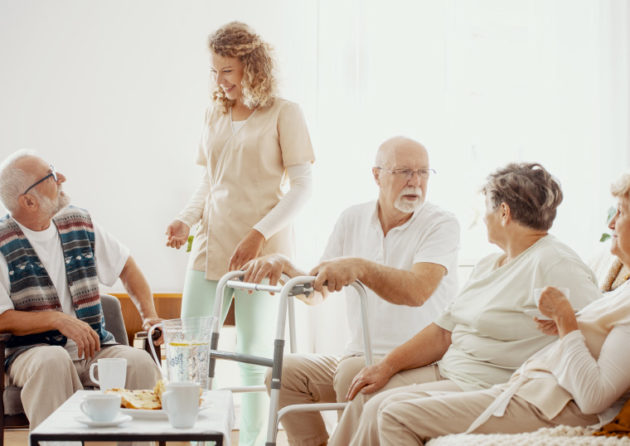

COMMUNITY
- Improving indoor air quality, reducing human smells and reducing the risk of infection among themselves.

RETAIL
- Lower health risk for employees who constantly come into contact with customer traffic and provide advice.
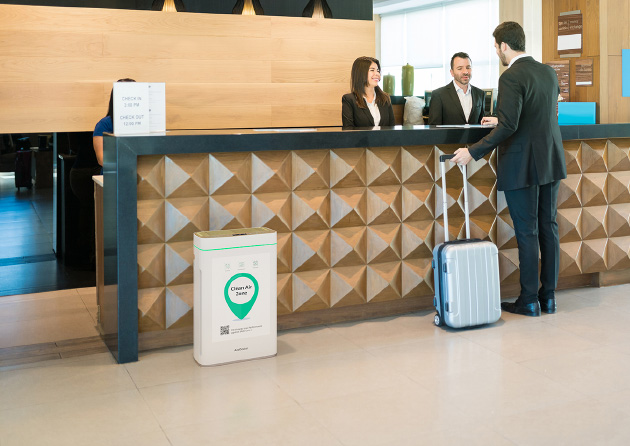

HOSPITALITY
- Reduction of the risk of infection in hotels, restaurants and all types of hospitality.
DELIVERING INNOVATION
Sustainability Goals
We are focused on building a long-term, sustainable business.
CAREERS

Let's grow
together
Join our international team and enjoy a creative, dynamic and inclusive culture focused on one goal – improving the world around us through imagination and innovation.






SCIENTIFICALLY VERIFIED



CERTIFIED ON ISO

Quality
Management Systems

Medical Devices:
Qualified Management Systems

Environmental
Management Systems

Reduction of Culturable
Airborne Bacteria Indoors
IN THE MEDIA




 English
English
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 Français
Français
 Italiano
Italiano
 Español
Español
 한국어
한국어
 繁體中文
繁體中文
 Việt Nam
Việt Nam